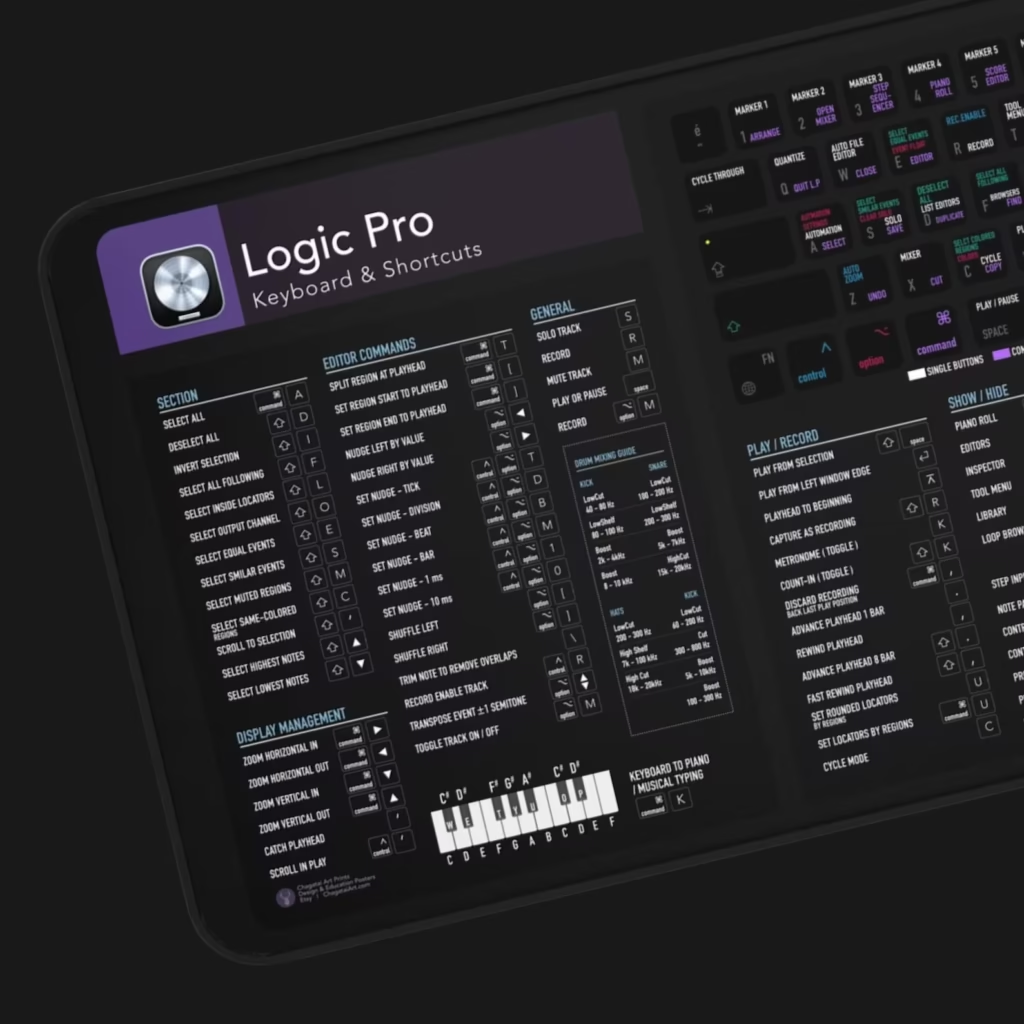
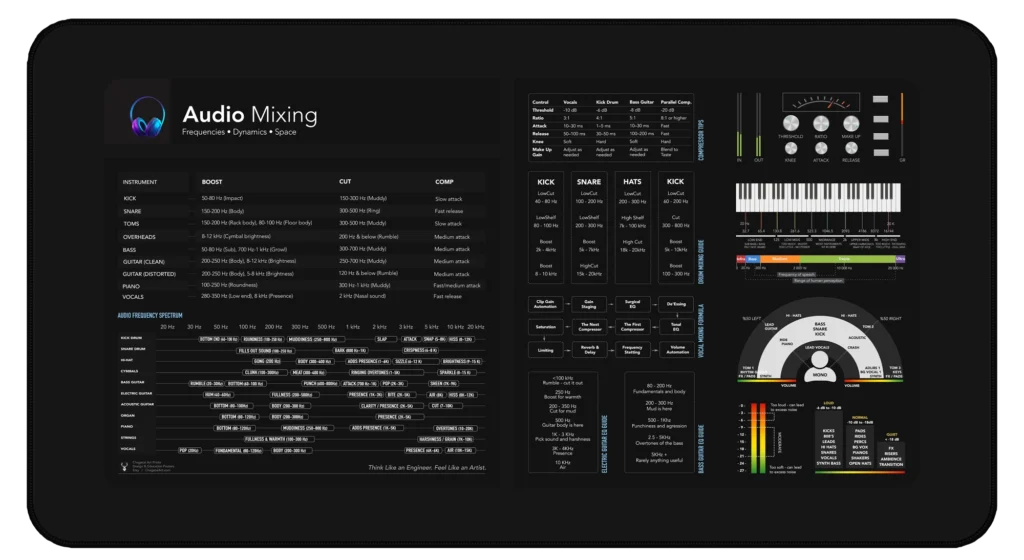
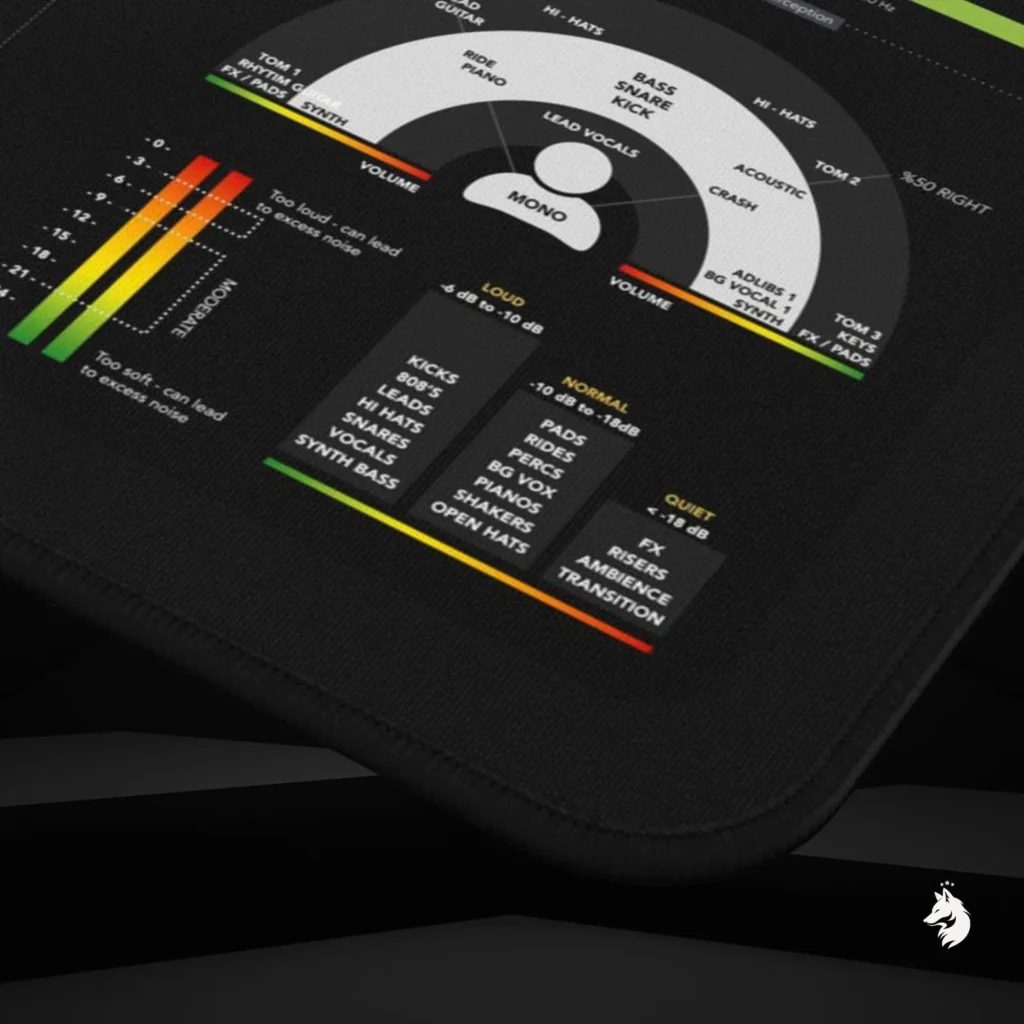
Mastering Low-End Balance: Kick and Bass in Perfect Harmony Audio...
Shop
Featured
Special Series
Champaigns
- Monochrome Art - Buy 3 Pay 2
- Students Get %20 Off
Shop
Home Collections
Life Style & Hobby
Info
Shop
Featured
Special Series
Champaigns
- Monochrome Art - Buy 3 Pay 2
- Students Get %20 Off